The modern water treatment process and Need
In cities like Spanish Fork, the growing population is putting pressure on the old system. The need for new plants for water treatment is being felt in place of the old plant, which has been operating since 1956, so that the Liquid can be cleaned in a better way.
Why are plants for water treatment important in initial cleaning?
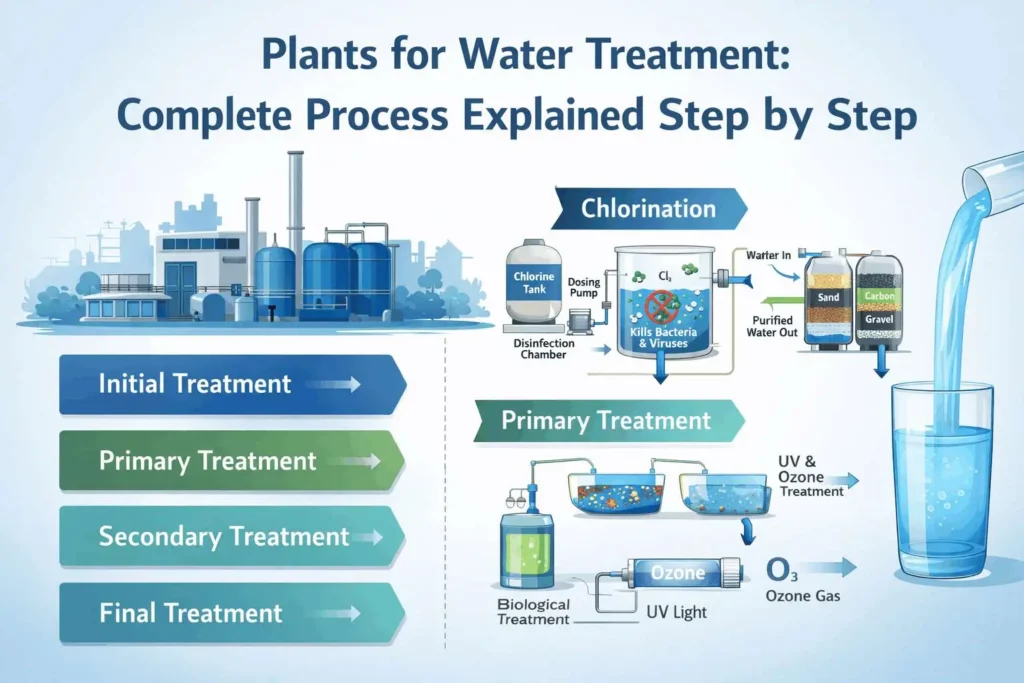
The treatment process starts when the sewage water enters the plant. First of all, ‘step screens’ are used to prevent large waste such as diapers, wipes, and other solids. The water then flows into the ‘grit chamber’ where the soil and pebbles settle to the bottom. This initial phase is necessary to protect the infrastructure of the plants for water treatment so that further machinery is not damaged.
How do primary clarifiers work?
After leaving the grate chamber, the water goes to the primary clarifier. Here, heavy solids, called ‘sludge’, settle down with the help of gravity. About 90-95% of settling solids are separated in this process of about 5 to 6 hours.
Do bacteria have any role in plants for water treatment?
Yes, ‘good bacteria, ‘ i.e., microorganisms, play a big role in purifying water. In ‘aeration basins’ (aeration basins), these microorganisms are given air and food (sewage waste), through which they eliminate harmful elements and chemicals like ammonia.
How is chlorination and final purification done?
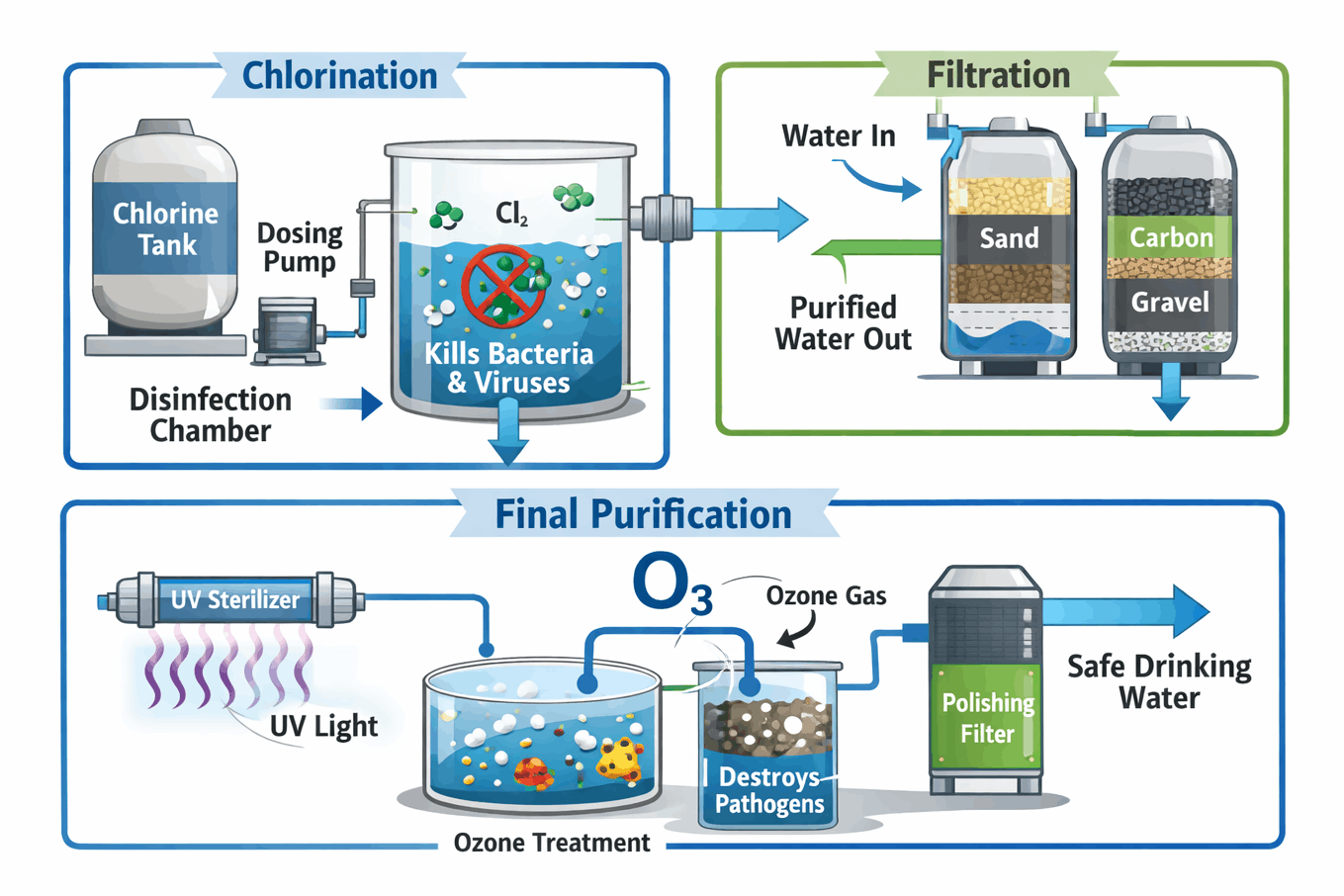
After being cleaned by bacteria, the water goes to the ‘secondary clarifier’ and then to the ‘chlorine contact basin’. Here, chlorine is added to the water to eliminate residual contamination. Clean water is released into rivers or drains only after proper disinfection.
Why is there a need for new plants for water treatment?
Older systems, such as ‘trickling filters’, no longer meet modern standards and nutrient removal requirements. Construction of advanced plants for water treatment for future needs and protection of the environment is the need of the hour.
The journey from wastewater to drinking water
Water treatment is not limited to dirt removal, but is a complex scientific process. Modern plants for water treatment use advanced technologies to process solid waste and produce potable water.
How does an anaerobic digester work?
When the sludge is separated from the water, it is sent to a ‘digester’. Unlike an aeration basin, here the ‘anaerobic’ process takes place, i.e, treatment without air. This process works exactly like the human digestive system. In plants for water treatment, this sludge is kept for at least 15 days, where microorganisms convert it into fertilizer.
What is the use of Bell Press (Belt Press)?
The waste coming out of the digester has a high water content. A ‘belt press’ machine is used to dry it. Here, the waste is pressed between the layers, increasing it from 4% solids to 18% solids. Better plants for water treatment ensure that the final material is clean enough not attract flies or rats.
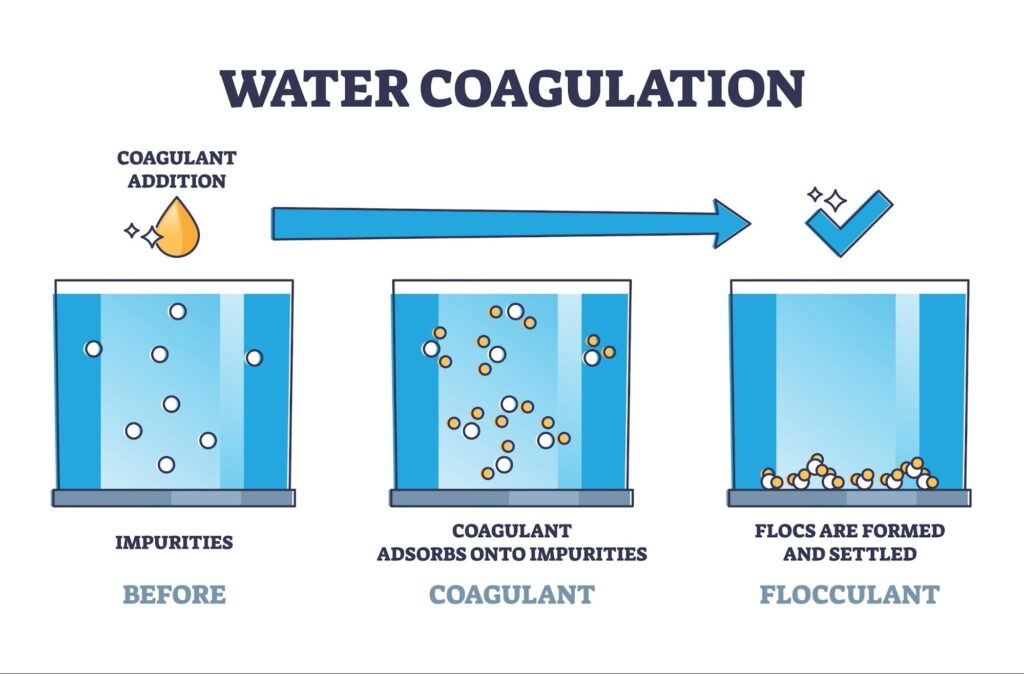
Is the process of coagulation necessary in purification?
Coagulation & Flocculation is used to purify drinking water. Clay and sand particles in water have an electrical charge that repels them. In plants for water treatment, oppositely charged chemicals are added so that these particles stick together to form heavy ‘floc’ and settle down easily.
What is Ozonation and Carbon Filtration?
Ozone gas is used to eliminate odors and bacteria from water. Ozone molecules destroy the cell wall of bacteria. After this, the water passes through the activated carbon and sand layers. In plants for water treatment, carbon filters absorb chemicals, and sand traps metal particles.
Why is UV treatment considered the last step?
Even water that looks perfectly clean can contain microscopic viruses. In the final step, the water is passed through a bank of ‘ultraviolet’ (UV) lights. This light destroys the DNA of pathogens, making the water completely safe.
From Sewer to Nature: The Final Cycle of Purification
Modern plants for water treatment not only clean the water, but also ensure that the water returned to nature is safe and balanced.
How is waste prevented in Headworks?
The first and most important part of purification is the ‘headworks’. Here, heavy mechanical ‘screw pumps’ raise the water and ‘bar screens'(Bar Screens) intercept large wastes such as diapers and clothes. An automatic ‘rake’ keeps these bars clean. This part of the plants for water treatment is the most important to protect the machinery from damage.
What is Great Chamber and Axial Vortex?
A ‘grit chamber’ is used to remove heavy particles such as sand, pebbles, and egg shells from the water. Here, a rotating ‘impeller’ creates a vertical spiral force, i.e. ‘axial vortex’. In plants for water treatment, this technique forces the heavy particles to hit the wall and settle down, while the lighter organic matter moves forward.
How are oils and greases removed in primary clarification?
When the water reaches the large circular ‘sedimentation tank’, it is slowed down. Here, floating substances like oil and grease rise to the top, which are removed with the help of a ‘skimmer’. Heavy solids settle to the bottom as ‘sludge’. This system of plants for water treatment starts to make the water transparent.
How do microorganisms eliminate dirt?
During ‘secondary treatment’, water is sent tothe’aeration tank’. Here are added helpful bacteria and protozoa that eat human waste and waste like soap. Air is rapidly pumped into the tank to keep these microorganisms alive. This biological process in plants for water treatment is the most effective way to eliminate dirt without chemicals.
How is treated water released into nature?
After final purification, the water passes through a ‘UV light’ and is then released into rivers or lakes through a special ‘outfall pipe’. These pipes are fitted with ‘diffuser nozzles’ which mix clean Liquid slowly and evenly into the environment. Modern Infrastructure for water treatment ensures that the discharged water does not disturb the natural balance.
By: Techy Content